Supply Chain Management (SCM): Component, Challenges & Trend
Understanding Supply Chain Management (SCM) has become more critical than ever when businesses find ways to optimize supply in global markets. So, come with Skilltrans to study the fundamentals of SCM, breaking down its five core components, and the benefits it offers.
We’ll also analyze emerging trends shaping the future of supply chains, the challenges companies face in maintaining efficiency, and the strategies needed to overcome them. Let’s get started!
What is Supply Chain Management (SCM)?

Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the process of planning, coordinating, and overseeing the flow of goods, services, information, and finances across the entire supply chain. It encompasses all activities in sourcing raw materials, manufacturing products, managing inventory, and delivering finished goods to the end consumer.
SCM optimizes efficiency and reduces costs by integrating key components such as procurement, production, logistics, distribution. Modern SCM often leverages technology, like AI, IoT, blockchain to improve visibility, decision-making, and operational efficiency.
What Are the Five Components of Supply Chain Management?
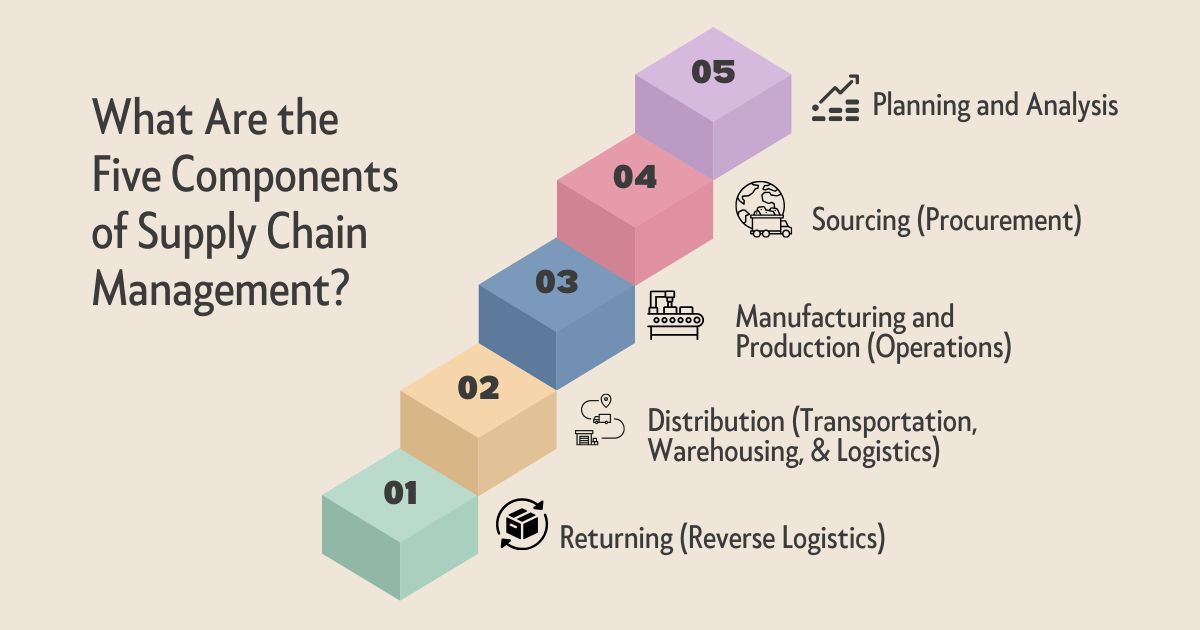
The five key components of Supply Chain Management (SCM) are:
Planning and Analysis
One critical aspect is demand forecasting. You can use historical data, market trends, and advanced tools such as predictive analytics and AI to predict customer requirements.
The implementation process is production planning scheduling manufacturing activities, managing labor, and utilizing resources efficiently. It makes production meet delivery timelines while controlling costs.
Additionally, distribution planning also can not be ignored, which creates the timely delivery of products to customers. You need to manage transportation logistics, warehouse operations, and optimize routes, carriers for cost-effectiveness. Finally, risk planning is integral to anticipating and mitigating potential disruptions such as supplier failures, natural disasters, or market volatility.
In terms of Analysis in Supply Chain Management (SCM), you need it to transform data into actionable insights that optimize operations and support better decision-making. A key focus area is performance metrics analysis, which evaluates efficiency indicators like inventory turnover, order accuracy, lead times, and fill rates. For instance, a high inventory turnover may signify efficient inventory management, while prolonged lead times could indicate bottlenecks.
Cost analysis examines expenses across procurement, production, warehousing, distribution to identify cost drivers and areas for potential savings.
Demand and supply variability analysis helps businesses understand fluctuations in demand and supply. Supplier performance analysis evaluates metrics such as reliability, lead times, quality, and costs. Scenario and predictive analysis go further by leveraging advanced tools like machine learning and simulation modeling to anticipate disruptions, test alternative strategies, and make proactive decisions to enhance resilience.
Sourcing (Procurement)
Sourcing identifies, acquires, and manages the suppliers needed to produce goods or services. This process is an important link to the supply chain to have the right materials, products, services at the right time, and at the best possible cost. Effective sourcing maintains operational efficiency, cost management, and the overall success of the supply chain.
The most essential step you must take is supplier selection and management. You evaluate potential suppliers based on criteria such as cost, quality, reliability, and sustainability. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers to a steady flow of materials and mitigate risks such as delays, quality issues, or disruptions in supply.
We all live by the law. So, companies must adhere to regulations and ethical standards, including labor laws, environmental sustainability, or fair trade practices. Many businesses prioritize suppliers that align with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals, enhancing their reputation and building trust with customers.
Manufacturing and Production (Operations)
Manufacturing and Production (Operations) in Supply Chain Management (SCM) are the processes that convert raw materials into finished goods. It is a core function that directly impacts the efficiency, cost, and responsiveness of the entire supply chain.
Effective manufacturing begins with meticulous planning and scheduling. You must analyze demand forecasts, allocate resources like labor, machinery, materials, and create production schedules that align with customer requirements. Advanced tools, such as Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems, are often used to synchronize production activities with supply chain timelines, minimizing delays and optimizing resource utilization.
So, how to optimize process optimization? Manufacturers employ methodologies like Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma to eliminate waste, reduce production time, and enhance efficiency. Automation technologies (robotics, AI) further streamline production processes, enabling consistent output and lower operational costs.
Manufacturing is deeply interconnected with other supply chain components. Close collaboration with sourcing ensures a steady flow of raw materials, preventing production disruptions. Integration with logistics helps manage inventory levels and coordinates the delivery of finished goods to distribution centers or end customers. Advanced data-sharing platforms and IoT-enabled systems enhance this integration by providing real-time visibility across the supply chain.
Distribution (Transportation, Warehousing, & Logistics)
Transportation selects appropriate modes of transport (road, rail, air, sea) based on cost, speed, and distance. Effective transportation management optimizes routes, reduces fuel consumption, and ensures timely deliveries. Advanced technologies enhance visibility, real-time updates, and proactive issue resolution.
Warehousing is a hub for storing goods before they are distributed to retailers or customers. As an integral part of distribution, inventory management maintains optimal stock levels to meet demand without overstocking or stockouts. Accurate inventory control makes cash flow smooth operation and minimizes carrying costs while facilitating product availability for customers.
The final stage of the distribution process is last-mile delivery. It is often the most complex and costly part of the supply chain due to the need for precision and speed. Innovations like drones, autonomous vehicles, and crowd-sourced delivery models are transforming last-mile logistics to improve efficiency and customer experience.
Returning (Reverse Logistics)
Returning (Reverse Logistics) manages the flow of products from customers back to the business. This process handles product returns, repairs, recycling, and disposal. Reverse logistics contributes to customer satisfaction as well as aligns with sustainability goals by promoting resource recovery and waste reduction.
Businesses often implement systems to track and process returns efficiently, ensuring timely refunds, replacements, or credits.
As environmental regulations become stricter, businesses are responsible for making returned goods processed in an eco-friendly manner. For example, electronic waste must be dismantled, with valuable materials like metals being extracted and reused. Proper disposal practices reduce environmental impact also protect companies from legal and reputational risks.
Benefits of Supply Chain Management

Supply Chain Management (SCM) has an impact on span across operational efficiency, cost savings, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
SCM streamlines processes by integrating sourcing, production, and distribution. Efficient planning tools and technologies serve the needs of accurate demand forecasting, reducing delays and bottlenecks. Automation in logistics and inventory management minimizes manual errors, accelerates workflows.
Cost Savings
A well-managed supply chain reduces operational costs significantly. Optimized transportation routes lower fuel and shipping expenses, while efficient inventory management minimizes carrying costs. SCM also reduces waste by aligning production levels with demand, preventing overproduction or excess inventory.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
By SCM, you can faster responses to customer inquiries and complaints. When you meet delivery timelines and maintain product quality, you directly have customer trust.
Greater Flexibility and Agility
SCM supports businesses to adapt quickly to market changes and disruptions. Companies use data analytics and demand forecasting to adjust production schedules, inventory levels to meet fluctuating customer needs. It is a preparation for unforeseen events like supply shortages, natural disasters, or sudden changes in consumer behavior.
Better Collaboration and Communication
SCM fosters collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Integrated systems and shared data platforms enhance coordination so all stakeholders can work toward common goals. Improved communication reduces misunderstandings and strengthens relationships across the supply chain.
Risk Mitigation
SCM provides greater visibility into the supply chain. Based on that, businesses identify potential risks early and develop contingency plans. For instance, monitoring supplier performance or tracking shipment statuses address issues proactively, avoiding costly disruptions.
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Businesses adopt sustainable practices by reducing waste, optimizing resource usage, and promoting recycling. Efficient logistics reduces carbon emissions, while reverse logistics facilitates the reuse and recycling of materials. These practices beautify a company’s reputation as a responsible corporate entity.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations with efficient supply chains are better positioned to compete in the market. They can deliver products faster, reduce costs, and offer better prices or value-added services to customers. This advantage often translates into increased market share and profitability.
Enhanced Data Utilization and Decision-Making
SCM leverages advanced technologies (IoT, AI, big data analytics) to provide actionable insights. Businesses use real-time data tracking and analysis to improve decision-making across the supply chain. These insights support businesses in optimizing processes and responding proactively to challenges.
Compliance and Risk Reduction
SCM adherence to legal and regulatory requirements by maintaining transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain. It is especially important in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, where compliance is critical to avoid legal and financial repercussions.
5 Key Trends in Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management trends respond to technological advancements, environmental concerns, and global uncertainties.
Increased Adoption of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML support businesses in forecasting demand more accurately, optimizing inventory levels, and reducing waste. AI strengthens operational efficiency. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and predict potential disruptions. You will have proactive responses to minimize delays or downtime.
Sustainability and Green Supply Chains
Sustainability is no longer optional—it's a business imperative. Companies are rethinking their supply chain strategies to align with global sustainability goals. This process is more diverse than many people think - reducing single-use plastics, employing energy-efficient transportation, adopting renewable energy in warehouses.
Supply Chain Resilience and Risk Management
The COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions have exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains. When the problem needs to be solved, businesses find a way to prioritize resilience. They diversify suppliers, nearshoring production, and implementing digital twin technology to simulate and test supply chain scenarios. Building resilience preventing crises and maintaining continuity in an increasingly uncertain world.
Integration of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology revolutionizes supply chain transparency and security. Blockchain maintains a decentralized, immutable ledger of transactions. It leads to every step in the supply chain - production, shipping, and delivery - is documented, verifiable. This level of transparency combats counterfeit goods, makes product authenticity, and simplifies compliance with regulations.
Emphasis on Digital Transformation and Smart Warehousing
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, robotics, and automation is driving the evolution of smart warehouses. IoT-enabled sensors provide real-time data on inventory levels, equipment status, and environmental conditions. Robotics and autonomous vehicles streamline tasks like sorting, packing, and transporting goods, reducing labor costs. Cloud-based platforms further enhance visibility across the supply chain.
Challenges of Supply Chain Management

To build efficient supply chains, businesses might to understand and address these issues.
Demand Forecasting and Variability
Unpredictable consumer behavior, market trends, and external factors like economic downturns or pandemics make forecasting a significant challenge. Inaccurate predictions can lead to overstocking, stockouts, or lost sales.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chains are vulnerable to disruptions caused by natural disasters, geopolitical conflicts, pandemics, and transportation issues. These disruptions can cause delays, increased costs, loss of revenue. Building resilience through diversification and contingency planning is essential but often complex.
Managing Costs and Budget Constraints
Rising fuel prices, labor costs, and raw material expenses exert pressure on supply chain budgets. Balancing cost efficiency with quality and timely delivery remains a persistent challenge, particularly in highly competitive markets.
Sustainability and Ethical Compliance
Nowadays, businesses must face growing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, doing eco-friendly operations and ethical sourcing. Besides, compliance with environmental regulations and transparency in production processes can be resource-intensive.
Technological Integration and Data Management
While digital transformation offers numerous benefits, integrating new technologies into existing supply chain operations can be challenging. Legacy systems, data silos, and lack of technical expertise hinder seamless adoption. Additionally, managing and securing vast amounts of supply chain data requires robust infrastructure.
Globalization and Geopolitical Risks
Global supply chains are exposed to risks such as trade wars, tariffs, and regulatory changes. Navigating complex international regulations and dealing with currency fluctuations further complicate global operations.
Customer Expectations for Speed and Transparency
Modern consumers demand faster delivery times and real-time tracking of their orders. Meeting these expectations requires advanced logistics, precise inventory management, and efficient last-mile delivery solutions, all of which pose operational challenges.
Inventory Management and Optimization
Maintaining the right balance between supply and demand is a constant struggle. Overstocking ties up capital, while understocking can lead to missed sales opportunities. Optimizing inventory levels in a dynamic market environment is a critical task.
Supplier Relationship Management
Establishing and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is crucial for a smooth supply chain. Issues such as unreliable suppliers, delayed shipments, or quality inconsistencies can disrupt operations and damage customer satisfaction.
Cybersecurity Risks
As supply chains rely more on digital systems, they become increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive data and making uninterrupted operations need robust cybersecurity measures.
Some of Skilltrans' courses might be helpful to you. Please click on the course name below to learn more.
How to Transition to Product Management (And Succeed)
By going through the course you will learn 3 strategies on how you can build up your product management expertise to successfully transition to the Product Manager (PM) role. Also, you will complete a practical exercise to assess your current skills and find transferable skills you already have to apply for the PM position.
Beginning Project Management: Project Management Level One
In this course, we’ll examine the absolute basics of project management. Everyone has to start somewhere, right? In this fundamental course, we will explore the big picture of project management and the project management life cycle. You’ll finish this course with an excellent grasp of project management, your roles and responsibilities as a project manager, and how to move forward in your career as a project manager.
This course is designed for people that are new to project management. This course is structured to give you a solid project management foundation and help you speak the project management language. Don’t worry – this course is easy to follow, has a logical approach, and it has a fun, can-do attitude in its delivery.
Become a Product Manager | Learn the Skills & Get the Job
The demand for Product Management is increasing at an insane rate. More and more companies are finally figuring out how important this discipline and this role is to their success.
But how exactly do you get into the field? There aren't any degrees in Product Management & there are no certifications. Most Product Managers get into the field through luck or connections. That ends here - we'll get you up to date on ALL the skills you need to learn Product Management AND have the best chance at getting the job you want. There's no more ambiguity to it. We'll show you what you need to know and what you have to do - all taught from a Product Management insider.
Conclusion
The thriving landscape of Supply Chain Management gives more opportunities for innovation but also presents challenges that demand strategic planning and resilience. Companies that stay ahead of these trends, address challenges proactively, and embrace sustainability will position themselves for long-term success.
If you want to gain more in-depth knowledge about supply chain management, you can register for Skilltrans courses. Come to us to open up your horizons of knowledge!

Meet Hoang Duyen, an experienced SEO Specialist with a proven track record in driving organic growth and boosting online visibility. She has honed her skills in keyword research, on-page optimization, and technical SEO. Her expertise lies in crafting data-driven strategies that not only improve search engine rankings but also deliver tangible results for businesses.



