What Are Hubs and Switches? Difference between Hub And Switch
If you are interested in networking devices, you may have heard of the two terms hub and switch. But do you know what hub and switch are? What is the difference between hub and switch? This article will explain in detail, including definitions, differences, advantages, disadvantages, installation, usage, troubleshooting, types, and how to choose and connect standards. After reading this article, you will have more knowledge of using hub and switch effectively.
What is Hub?

Hub is a network device to connects other computers/devices on the same LAN. It includes 4 to 24 ports. The hub is the center that connects and transmits data to other ports.
However, it sends all data at the same time because it does not assign tasks to any port. Hub helps connect devices such as printers, I/O devices, and storage devices.
Currently, Routers are commonly used, and Switches replace Hubs in families. But with low cost, Hubs still play an important and necessary role for certain purposes, servers in data centers.
What are the characteristics of Hub?
Hub has many ports from 4 - 24 ports, even more. Most hubs use 10BASE-T or 100BASE-T networks. It is in the center and helps create Point to Point links.
Here are some characteristics of Hub:
Operate with shared bandwidth, broadcast.
Operate at the physical layer of the OSI model, support half-duplex mode.
Can cause conflicts in the transmission line of many computers.
Flexible, high speed.
What are the applications of Hub?
Some applications of Hub today:
Create small home networks.
Network monitoring.
Provide connectivity in organizations/enterprises.
Create a device available.
The Role and Function of Hub
Hub processes data called “frames” and amplifies them to the computer ports. Hub will have Frames transmitted, and most likely Broadcast to the ports. Hub will transfer to the ports, the traffic on the network is quite high, so it is easy to cause slow response time.
Advantages of Hub
Hub has the following advantages:
Supports different network media.
Low investment cost, so many people use it.
Network performance is not affected by one.
Easy to extend the distance of the network.
Disadvantages of Hub
Besides the above advantages, Hub also has the following disadvantages:
Inability to choose the best path of the network.
Unable to detect conflicts, reducing network traffic.
Unable to filter information.
No ability to connect network architectures (ring, token, ethernet, etc).
Benefits of using Hub
Switches have become the preferred choice for most network environments. They bring many benefits:
Fast transmission speed
There are many classes of Hubs with different speeds such as class 1 with a delay of 140-bit time and class 2 with a delay of 92-bit time.
Dual Speed operates on 10M/bit, 100M/bit segments. The ports will operate and transmit at higher speeds when in this segment. It can also lead to model errors because they cannot create Switches between traffic streams.
Error detection and prevention
Hubs can detect major errors, major collisions, and intermittent collisions of ports and it will cut off the signal flow, isolating that device immediately.
Hubs want to transmit data, so they must be the same in every segment and repeaters cannot link data to other segments.
What is the speed of the Hub?
Ethernet Hub speeds vary in terms of network and bandwidth. Early Hubs had speeds of 10Mbps and 100Mbps. Hubs had different numbers of ports such as 4, 5, 8, and 16 ports.
Home networks would use fewer ports, while larger businesses would use more ports. Older Hubs had noisy cooling fans and were large in size, while modern Hubs were quiet, compact, and easy to move.
How to work with Hubs
First, you need to connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the device and plug the other end of the cable into the Hub's NIC (Network Interface Card). The port on the Hub fits the Ethernet's RJ45 cable. If you want to expand the network to connect more devices, you can link the Hubs together or connect the Hub Switch or Router.
What is a Switch?

The switch is a networking device that connects multiple devices on a computer network. A switch also has multiple ports, but unlike a hub, a switch has the ability to learn and store the MAC (Media Access Control) addresses of connected devices.
The switch operates on the Datalink layer of the OSI model, meaning it can distinguish the source and destination addresses of data packets, and only forward data packets to the corresponding destination port. The switch uses Full-duplex cables, it can transmit and receive data at the same time, increasing data transmission efficiency. The switch is also known as a switching device, because it can create separate transmission channels between connected ports, reducing collisions and interference.
Advantages of Switches
Some of the advantages of switches are:
Ability to learn and store MAC addresses, helping to transmit data accurately and quickly.
Ability to create separate transmission channels, benefit increased bandwidth and network performance.
Ability to filter data, aiding in reducing conflicts and interference in the network.
Ability to connect different network architectures, assisting in creating virtual LANs (VLANs).
Disadvantages of Switches
Some of the disadvantages of switches are:
Higher cost than hubs and is more difficult to use.
Can be attacked by spoofing MAC addresses.
Can be overloaded by large network traffic.
Similarities between Hub and Switch
Hub and Switch are similar:
Connect multiple computers or electronic devices on the same network.
Amplify signals and packets to ports.
Differences between Hub and Switch
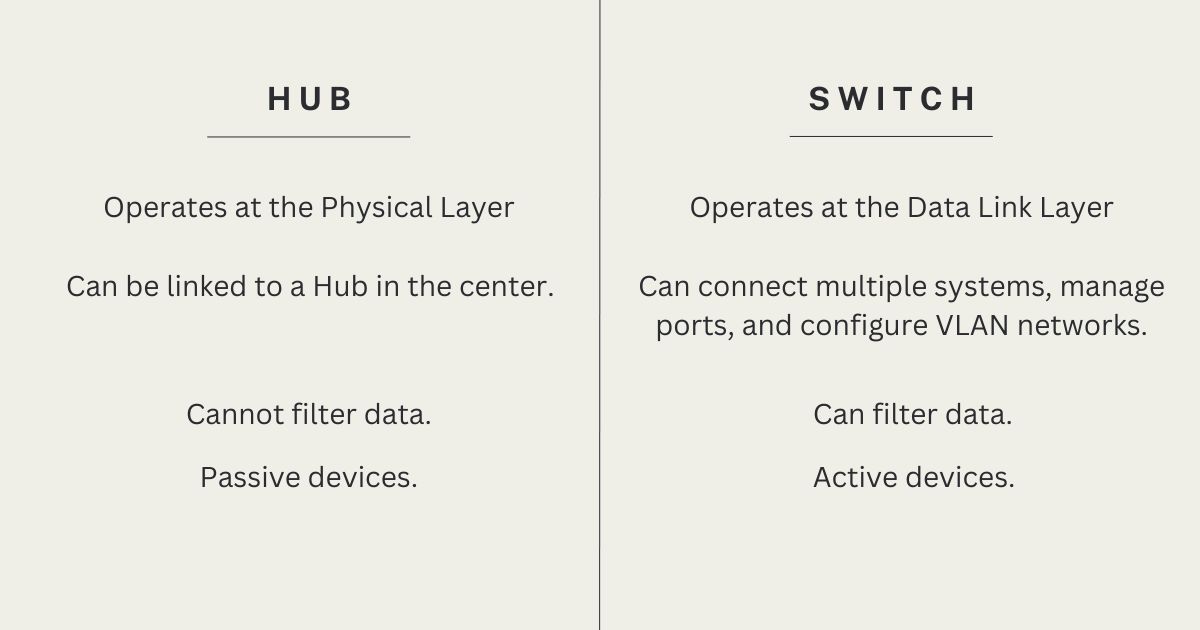
In addition to the fact that Hub and Switch have in common the central connection for network devices and receive data from one port and send it to other ports, they have differences such as:
| Hub (Network splitter) | Switch (Network switching device) |
| When data enters the Hub, it will be transferred to all the remaining ports and does not understand which port is the information destination, so it is easy to conflict with the network. | When data enters the Switch, it will check the data and determine the data source and data destination to send to the correct port. Therefore, it avoids information conflicts. |
| Hub runs in Half Duplex mode (it only transmits/receives). | Switch runs in Full Duplex mode (transmits and receives at the same time). |
| Operates at the Physical Layer | Operates at the Data Link Layer. |
| Can be linked to a Hub in the center. | Can connect multiple systems, manage ports, and configure VLAN networks. |
| Cannot filter data. | Can filter data. |
| Data/information is transmitted in the form of bits, and electrical signals. | Data/information is transmitted in the form of Frames/Packets. |
| Passive devices. | Active devices. |
| Has half-duplex mode. | Has full-duplex or half-duplex mode. |
| The transmission speed is 10Mbps | Transmission speed is 10Mbps – 1Gbps. |
Should you use a Hub or a Switch for your network system
You should use a Hub if you need to diagnose a protocol in a Plugfest and it will operate at only 1 speed, and half-duplex mode in Shared Ethernet. Moreover, the diagnostic tool can receive messages. Switch limits port traffic so that the diagnostic tool cannot see messages, except Broadcast messages.
For connecting to many devices, Switch is the most suitable choice. The Switch has full features. Switches can operate at multiple data rates in half-duplex or full-duplex mode. Switches improve by limiting the amount of direct message traffic sent by the master to which the Switch participates in communication.
Conclusion
While both hubs and switches are essential networking components, they operate at different levels and offer distinct functionalities. Hubs operate at the physical layer, broadcasting data to all connected devices, leading to potential network congestion and performance issues. On the other hand, switches operate at the data link layer, intelligently forwarding data packets to their intended destinations, enhancing network efficiency and performance. Understanding these differences is crucial for building robust and efficient network infrastructures.
To learn more about this knowledge, you can register for Skilltrans courses. We have worthwhile courses at affordable prices.

Meet Hoang Duyen, an experienced SEO Specialist with a proven track record in driving organic growth and boosting online visibility. She has honed her skills in keyword research, on-page optimization, and technical SEO. Her expertise lies in crafting data-driven strategies that not only improve search engine rankings but also deliver tangible results for businesses.



