Early Childhood Care and Education: Importance & Challenges
The early years of a child's life are a whirlwind of growth and discovery. From babbling their first words to taking their first steps, these formative years lay the foundation for everything that comes next. During this critical time, Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) plays a vital role in nurturing young minds and setting them on a path to lifelong success.
This article delves into the world of ECCE, exploring its significance and the essential components that make it effective. We'll also examine the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, where innovation and collaboration are paving the way for a brighter tomorrow for all children.
So, whether you're a parent, educator, or simply someone who cares about the well-being of future generations, join us as we explore the fascinating world of Early Childhood Care and Education.
What is Early Childhood Care and Education?
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) refers to the comprehensive care and learning experiences offered to young children, typically from birth up to the start of 8 years old. This period is recognized as a critical phase for establishing a strong foundation for lifelong learning, well-being, and overall development. ECCE encompasses a wide range of programs and services that focus on a child's overall well-being, including:
Cognitive development: Through play-based activities and stimulating environments, ECCE programs help children develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and language skills.
Social and emotional development: Interaction with peers and qualified caregivers fosters social skills like sharing, collaboration, and emotional regulation.
Physical development: Activities that encourage movement and exploration help children develop motor skills and coordination.
Here's a breakdown of the different settings where ECCE takes place:
Center-based care: Daycare centers and preschools, where children participate in structured activities and group learning under the supervision of qualified caregivers.
Home-based care: Nannies or parental guidance programs that provide support and resources for families raising young children at home.
Community-based programs: Playgroups, early intervention programs, and library story times are all examples of community-based ECCE initiatives that offer socialization and learning opportunities for young children.
Components of Effective ECCE Programs
Effective early childhood care and education (ECCE) programs are built on several key components that ensure the holistic development and well-being of young children. These components work together to create an enriching, supportive, and inclusive environment. Here are the essential components of effective ECCE programs:
Developmentally Appropriate Curriculum

At the heart of a successful Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) program lies a developmentally appropriate curriculum. This curriculum recognizes that children learn and grow at their own pace, and it caters to their specific needs and interests across various developmental domains.
Focus on Play-Based Learning
Play is a child's natural way of exploring the world and acquiring new skills. A developmentally appropriate curriculum prioritizes play-based learning through activities that are engaging, and fun, and allow for exploration and experimentation.
Holistic Development: Play activities can nurture physical development (through active play), social development (through collaborative play), cognitive development (through problem-solving and exploration), and language development (through storytelling and pretend play).
Child-Led Exploration: The curriculum allows for child-initiated activities, where children have some control over what they learn and how they learn it.
Integration of Learning Domains
A developmentally appropriate curriculum recognizes the interconnectedness of different developmental domains. The curriculum should integrate various domains of development, including language, literacy, mathematics, science, social studies, and the arts, ensuring a well-rounded education. For example, reading stories (language) can spark imaginative play (social-emotional) and lead to discussions about characters' feelings (social-emotional).
Themes that capture children's interests can be used to integrate learning across different domains. For instance, a theme on "families" might involve art activities (creating family portraits), songs about families (language), and pretend play scenarios involving families (social-emotional).
Developmentally Appropriate Practices
Activities and materials should be tailored to the specific age and developmental stage of each child. The curriculum should challenge children without being frustrating, ensuring a sense of accomplishment and fostering a love for learning.
Qualified and Trained Educators

Qualified and trained educators are undeniably a cornerstone of effective Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs.
Understanding Child Development
Educators with a strong understanding of child development can create stimulating and age-appropriate learning experiences that cater to each child's cognitive, social-emotional, and physical needs.
Trained educators can recognize developmental milestones and potential delays, allowing for early intervention and support if necessary.
Effective Implementation of Curriculum
Educators trained in developmentally appropriate practices can effectively implement the curriculum, tailoring activities and assessments to individual needs and learning styles.
Through ongoing observation and assessment, qualified educators can track children's progress and adjust their teaching strategies to maximize learning outcomes.
Safe and Stimulating Environment

A safe and stimulating environment provides the foundation for positive learning experiences, fostering a child's physical, social-emotional, and cognitive development.
Promoting Safety and Security
The environment should be free from hazards and promote safe exploration. It must include age-appropriate furniture, proper supervision, and clear safety protocols.
Encouraging Exploration and Learning
A well-equipped environment offers a variety of stimulating materials and resources.
Designated Learning Areas: Clear and designated spaces for different activities, such as a reading nook, a block-building area, or an art studio, provide structure and encourage focused exploration.
Natural Light and Space: The combination of natural light and spaciousness significantly contributes to an environment where people can move freely and engage in exploratory activities.
Family and Community Engagement
Fostering strong family and community engagement creates a powerful support system that extends beyond the classroom walls, enriching a child's development in a multitude of ways. Parents should volunteer in the classroom, participate in events, or simply discuss learning activities at home.
Enhanced Learning: Parents are a child's first teachers, and their involvement at home reinforces concepts learned in ECCE programs. Moreover, a child feels secure and supported when their parents are actively involved in their education.
Stronger Communication and Collaboration: Regular communication between parents and educators leads to a better understanding of a child's individual needs and learning styles. This collaborative approach allows for tailored support and a more effective learning journey.
Inclusive Practices
Inclusive practices are fundamental for creating effective Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs. These practices ensure that all children, regardless of background, ability, or needs, feel welcome, valued, and supported in their learning journey.
Equitable Opportunities: Inclusive ECCE programs provide all children equal opportunities to participate in activities, learn, and develop to their full potential.
Valuing Individuality: Children with different abilities, backgrounds, and learning styles are celebrated for their unique strengths and perspectives.
Building Empathy and Understanding: Exposure to diversity fosters empathy, understanding, and respect for others. ECCE prepares children to become well-rounded and responsible citizens.
Focus on Health and Nutrition

Focus on health and nutrition lays the groundwork for a child's physical well-being, cognitive development, and overall ability to thrive in the learning environment.
Physical Growth and Development: Proper nutrition provides the essential nutrients for healthy growth. It ensures the comprehensive development of strong bones, muscles, and a healthy immune system.
Enhanced Brain Function: Nutritious foods fuel the brain, impacting memory, focus, and cognitive development. A well-nourished child is better equipped to learn and retain information.
Establishing Healthy Habits: ECCE programs that promote healthy eating habits set the stage for a lifetime of well-being. Children learn about healthy food choices and develop positive associations with nutritious meals.
ECCE program can create a nurturing environment that promotes physical activity and lays the foundation for healthy lifestyle habits in young children.
Healthy Development: Regular physical activity is essential for healthy development. It strengthens muscles and bones, improves coordination, and promotes a healthy weight.
Focus and Learning: Physical activity helps children release energy, improves focus, and enhances their learning ability. Movement breaks can be strategically incorporated throughout the day to optimize learning.
Balanced Meals and Snacks: ECCE programs should provide balanced meals and snacks that meet children's nutritional needs. Recommended foods are fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats.
Health Services: Regular health screenings, immunizations, and access to healthcare professionals are important for early detection and intervention of health issues.
Assessment and Evaluation
Within Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs, assessment and evaluation play vital roles. They are not synonymous but rather complementary practices that provide valuable insights into a child's development and the program's effectiveness.
Assessment: Understanding the Individual Child
Assessment is an ongoing process of gathering information about a child's development through observations, interactions, and portfolio building.
Focus Areas: Assessments can focus on various developmental domains, such as cognitive skills, social-emotional development, physical development, and language skills.
Identifying Strengths and Needs: Assessment helps identify a child's strengths, areas for growth, and any potential delays. This information allows for individualized support and targeted interventions if necessary.
Evaluation: Measuring Program Effectiveness
The evaluation assesses the effectiveness of the ECCE program itself. It includes examining how well the curriculum is implemented, the learning environment is designed, and the needs of all children are being met.
Outcomes and Impact: Evaluation goes beyond the individual child to look at the program's overall impact on children's learning and development.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Evaluation data can be used to inform improvements to the program's curriculum, teaching practices, and overall approach to ensure it meets the needs of all children.
Supportive Relationships
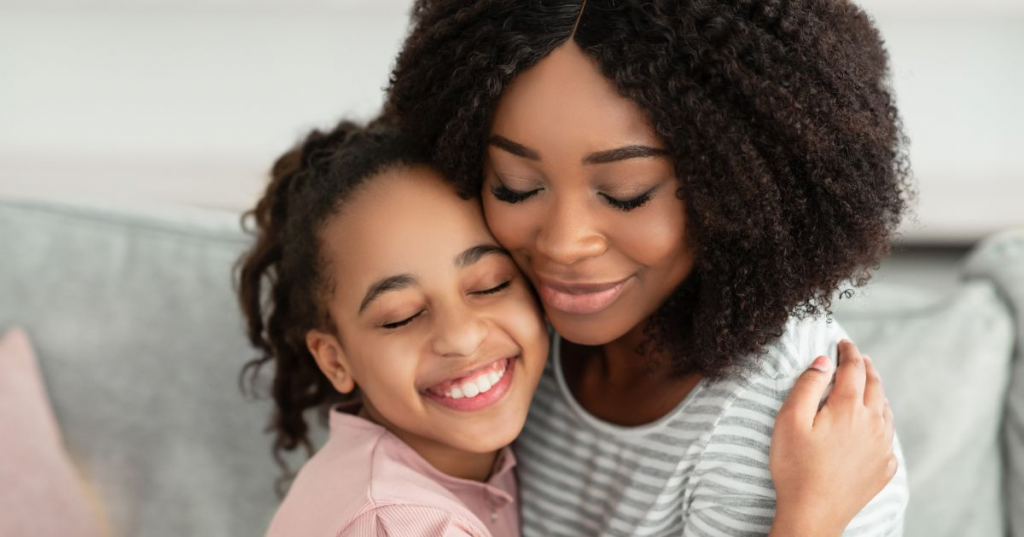

Supportive relationships are the cornerstone of effective Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs. These relationships provide a safe and nurturing environment where children feel valued, secure, and empowered to learn and grow.
Strong Bonds with Educators: Positive and trusting relationships between children and their educators create a sense of security and belonging. Children feel comfortable exploring, ready to take risks, and feel comfortable when asking questions.
Open Communication with Families: Strong partnerships between educators and families foster open communication and collaboration, ensuring a consistent and supportive approach to a child's development.
Positive Interactions: Through supportive interactions, children learn valuable social skills like empathy, cooperation, and conflict resolution.
Holistic Development Focus
A holistic approach goes beyond academics, addressing the physical, social-emotional, and cognitive needs of each child. It creates a well-rounded foundation for future learning and overall well-being.
Interconnectedness of Domains: The curriculum acknowledges the interconnectedness of these domains. For instance, physical activity can enhance cognitive function, and social interaction can influence emotional development. Learning experiences are designed to integrate these aspects for a comprehensive approach.
Personalized Learning: A holistic approach recognizes that children develop at their own pace and in their unique ways. Educators tailor activities and support to cater to individual strengths, learning styles, and needs.
Enhanced Learning: When children feel physically comfortable, safe emotionally, and have their social needs met, they are better equipped to focus, participate actively, and retain information. A holistic approach creates an environment conducive to optimal learning.
Examples of a Holistic Approach in Action
A holistic approach in action focuses on understanding and addressing the interconnected aspects of a situation rather than just treating individual parts in isolation.
Play-Based Learning: Play is a natural way for young children to learn and explore. Holistic ECCE programs integrate play-based activities that encourage physical development (through active play), social interaction (through collaborative play), creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Social-Emotional Learning: Programs that incorporate social-emotional learning activities help children develop self-awareness, manage emotions, build relationships, and make responsible decisions.
Integration of the Arts: Music, movement, and creative expression are incorporated into learning experiences, fostering creativity, imagination, communication skills, and emotional expression.
Physical Development: Opportunities for physical activity, both structured and unstructured, support motor skills and overall physical health.
Smooth Transitions
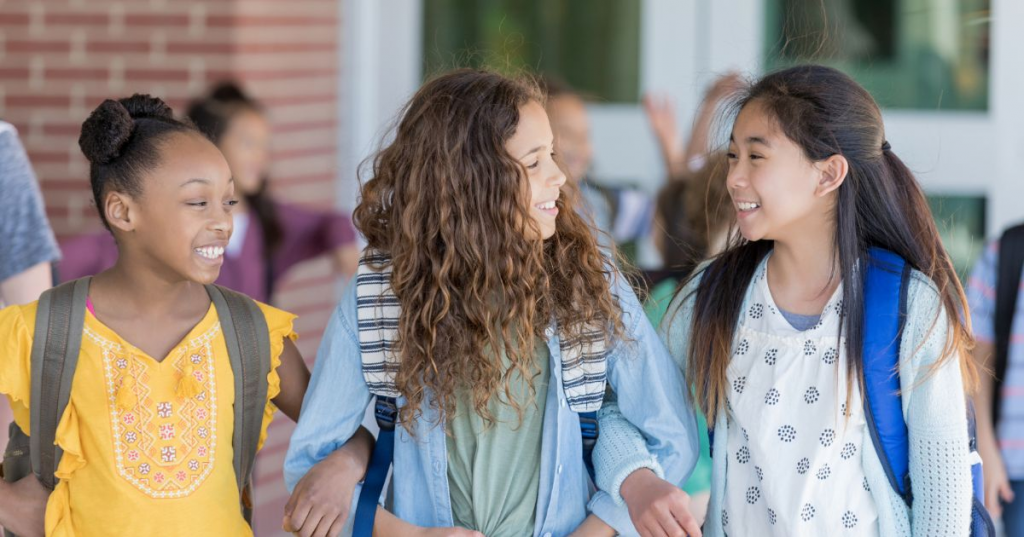

In the world of Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), smooth transitions are essential for ensuring a child's well-being and continued learning. These transitions can occur within the program itself (moving to a new classroom) or involve entering kindergarten.
Change Can Be Challenging: Transitions, even positive ones, can be unsettling for young children. A smooth transition process minimizes stress and anxiety, allowing them to feel secure and supported during this period of change.
Maintaining a Sense of Routine: Predictability and familiar routines provide comfort and a sense of security. Effective transition plans help children adjust to new routines and expectations.
Preparation and Familiarity: Preparing children for upcoming transitions through storytelling, role-playing, or visits to the new environment fosters a sense of familiarity and reduces apprehension.
Promoting Independence: Encouraging children to participate in self-care routines and decision-making during transitions empowers them and builds confidence.
By focusing on these essential components, ECCE programs can provide a strong foundation for lifelong learning, well-being, and success, ensuring that all children have the opportunity to reach their full potential.
Importance of Early Childhood Care and Education
The early years of a child's life, from birth to 8 years old, are a period of incredible growth and development. During this critical window, the brain rapidly forms connections that shape a child's cognitive, social, emotional, and physical well-being. High-quality Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs play a vital role in nurturing this development and providing a strong foundation for a child's future success.
Brain Development
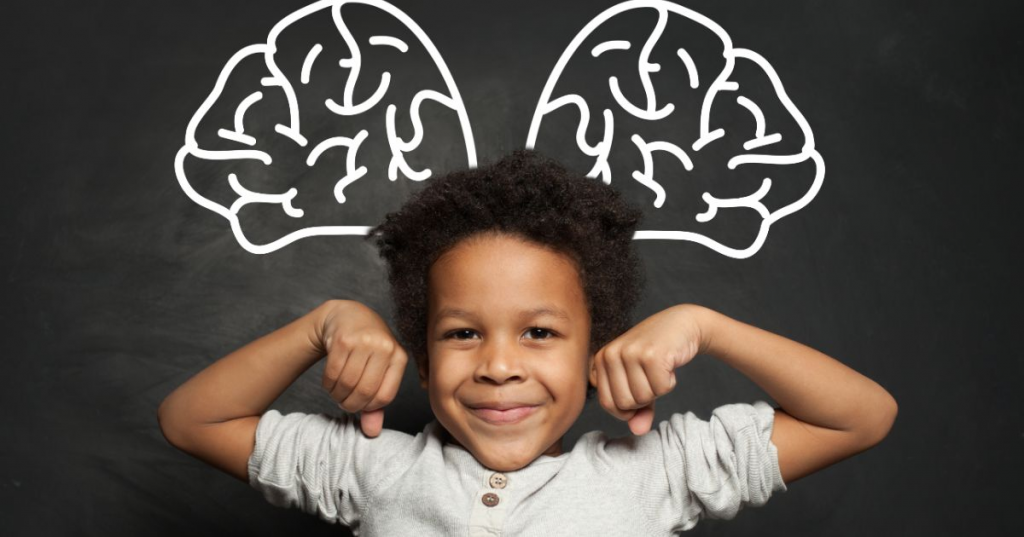

The brain develops faster in the early years than at any other time. By age 5, a child's brain has reached around 90% of its adult size. ECCE programs provide stimulating environments that nurture the formation of these crucial neural connections.
Quality ECCE programs stimulate cognitive development through engaging and appropriate activities. Play-based learning, exploration, and hands-on activities encourage curiosity and problem-solving.
Social and Emotional Development
During the early years, children experience a period of rapid social and emotional development. Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs play a vital role in nurturing these skills, laying the foundation for healthy relationships, emotional well-being, and overall success in life.
Safe and Secure Environment: ECCE programs strive to create a safe and secure environment where children feel comfortable exploring and interacting with others. This sense of security allows them to build trusting relationships with caregivers and peers.
Social Interaction and Collaboration: Through play-based activities and group projects, children learn to interact with others, share, take turns, and collaborate effectively. It fosters empathy, cooperation, and social skills crucial for building positive relationships.
Communication Skills: ECCE programs provide opportunities for children to practice communication skills through storytelling, singing, conversations, and dramatic play. Children can express themselves clearly, listen actively, and understand different perspectives.
Identifying and Labeling Emotions: Children learn to identify their own emotions and the emotions of others through stories, songs, and picture books. They learn to manage their feelings in healthy ways. It involves deep breathing exercises, positive self-talk, or seeking help from a trusted adult.
Building Independence: Gaining independence through tasks like self-care or completing projects contributes to a sense of self-efficacy and a positive self-image.
School Readiness
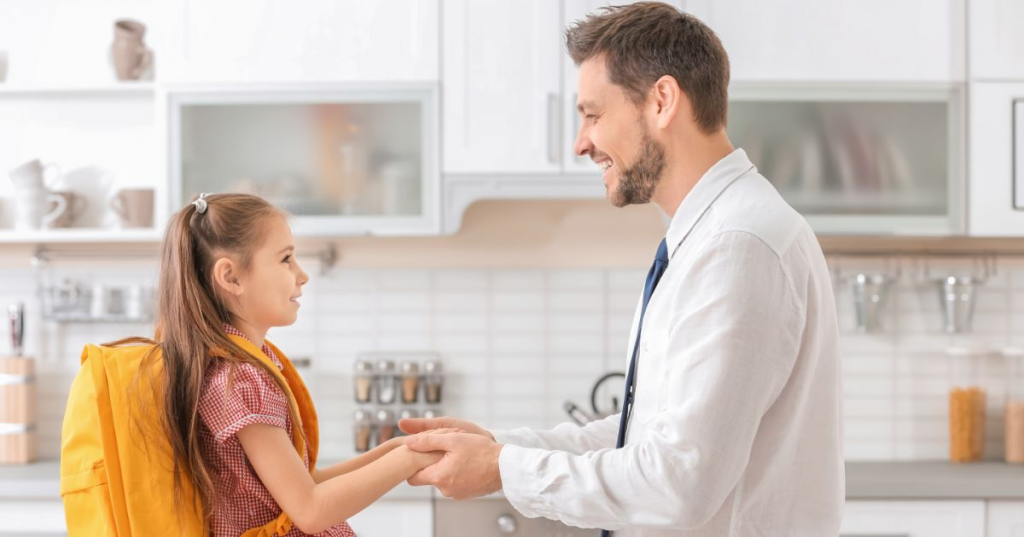

Early childhood care and education are fundamental in ensuring school readiness and providing children with the cognitive, social, emotional, and physical skills they need to succeed in school.
Cognitive Development: ECCE programs promote the development of essential cognitive skills language, literacy, math concepts, problem-solving, and critical thinking. These skills form the foundation for a child's ability to learn and succeed in academic settings.
Fine and Gross Motor Skills: Through play-based activities and creative exploration, children develop fine motor skills (e.g., grasping a pencil) and gross motor skills (e.g., balancing, jumping). These skills are necessary for tasks like writing, participating in physical education, and manipulating learning materials.
Structure and Routines: ECCE programs often introduce children to routines and expectations similar to a school setting. So, it helps them adjust to the structured environment and expectations of formal education. They enter school with a strong foundation for learning and a positive attitude towards education.
Social and Emotional Readiness: Children who have strong social and emotional skills are better equipped to handle the challenges and frustrations that may arise in school, leading to better academic performance.
Long-Term Benefits
The positive impact of Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) extends far beyond a child's early years.
Educational Attainment: Children who participate in quality ECCE programs are more likely to achieve higher educational levels. They perform better in school, have lower dropout rates, and pursue higher education.
Economic Outcomes: Early education is linked to better economic prospects in adulthood. Individuals with a strong early education foundation tend to have higher earning potential and more stable employment.
Health and Well-Being: ECCE promotes better physical and mental health outcomes throughout life. Early education instills healthy habits and reduces the likelihood of engaging in risky behaviors.
Economic Benefits: A well-educated workforce contributes to a stronger economy. Investing in ECCE can lead to increased productivity and reduced social costs in the long run.
Equity and Inclusion

In the realm of Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), achieving equity and inclusion is paramount. It ensures all children, regardless of background, have access to high-quality experiences that nurture their development.
Closing Achievement Gaps: Accessible ECCE programs provide opportunities for all children, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds, to develop their full potential. Early intervention can address developmental delays and support children with special needs.
Social Inclusion: Inclusive early childhood education fosters acceptance and appreciation of diversity, teaching children to respect and value differences from a young age.
Reduced Crime Rates: Research suggests that quality ECCE programs can have a long-term positive impact on behavior, potentially reducing crime rates later in life. By fostering social skills and emotional regulation, these programs help children develop into responsible citizens.
Holistic Development
In the early years, children experience a period of rapid and interconnected growth. Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs that embrace a holistic approach recognize this and aim to nurture all aspects of a child's development, not just cognitive skills.
Nurturing All Domains: Holistic ECCE programs go beyond academics, addressing the physical, social-emotional, and cognitive needs of each child. It creates a well-rounded foundation for future learning and overall well-being.
Building Strong Connections: For instance, physical activity can enhance cognitive function, and social interaction can influence emotional development.
Social and Emotional Well-being: Holistic ECCE programs that promote social interaction, emotional regulation, and self-confidence contribute to a child's social and emotional well-being, setting the stage for positive mental health throughout life.
Healthy Lifestyles: Developing healthy habits early on, through exposure to nutritious foods and physical activity, lays the foundation for a healthy lifestyle in the future.
Challenges and Opportunities of early childhood care and education
While ECCE offers a multitude of benefits for young children, there are challenges to address and exciting opportunities to consider when building a strong foundation for the future generation.
Challenges
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs, despite their immense benefits, face various challenges that can hinder their effectiveness. Here are some of the key hurdles that ECCE programs encounter:
Accessibility and Equity
Accessibility and equity are indeed major challenges faced by Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs.
Accessibility Challenges

Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs face several accessibility challenges.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: The cost of high-quality ECCE programs can be a significant burden for low-income families. Limited access to financial assistance or subsidies can create an economic barrier to participation.
- Geographic Limitations: ECCE programs may not be readily available in all communities, especially rural areas or underserved neighborhoods.
- Scheduling Constraints: Rigid program schedules may not accommodate the needs of working families, particularly those with non-traditional work hours or shift work.
Equity Challenges
These challenges can have a significant negative impact on a child's development and future opportunities.
- Cultural and Linguistic Barriers: Programs that are not culturally responsive or lack resources to support children with diverse backgrounds and languages can create feelings of exclusion and hinder learning.
- Disabilities and Special Needs: A lack of resources or qualified personnel trained to support children with disabilities or special needs can make it difficult for them to participate meaningfully in the program.
Quality and Standards
Ensuring that young children receive high-quality care and education is crucial for their development and future success.
Funding Limitations: Limited funding restricts resources needed for qualified educators, stimulating learning materials, and maintaining a safe and healthy environment.
Workforce Shortages: A shortage of qualified and well-compensated ECCE educators can lead to high staff turnover and a less stable learning environment for children.
Inconsistent Standards: Variations in national, regional, or licensing standards create inconsistencies in quality across different ECCE programs.
Opportunities
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) programs offer a multitude of opportunities that benefit not only young children but also society as a whole.
Innovative Practices
The field of ECCE is brimming with exciting opportunities for innovation. Here's a closer look at some innovative practices transforming ECCE:
Technology Integration

Technology integration in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) can be a powerful tool to enhance learning and development, but it's important to approach it thoughtfully.
Educational Apps and Games: Interactive apps and games can supplement traditional learning methods, fostering skills development in a fun and engaging way. However, it's crucial to ensure these tools are age-appropriate and used alongside other forms of play and exploration.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Emerging technologies like VR and AR have the potential to create immersive learning experiences that spark curiosity and exploration. Imagine children virtually traveling to different ecosystems or exploring the human body through AR!
Personalized Learning Platforms: Technology can be used to personalize learning experiences for each child. Adaptive programs can adjust content and difficulty to meet a child's individual needs and learning pace.
Focus on Nature and Sustainability
Incorporating a focus on nature and sustainability in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) is essential for fostering an early appreciation for the environment and promoting sustainable practices among young children.
Outdoor Classrooms and Nature Play: Immersing children in nature through outdoor classrooms and nature play fosters a connection with the environment, promotes physical activity, and encourages creativity and problem-solving skills.
Sustainability Education: Integrating sustainability concepts into the curriculum can teach children about environmental responsibility from a young age. Activities like composting, gardening, and learning about renewable energy can spark a lifelong commitment to caring for the planet.
Play-Based Learning with a Twist
Here’s how play-based learning with a twist can be implemented in early childhood care and education:
STEAM Education: Integrating Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Math (STEAM) concepts into play-based activities can nurture creativity, curiosity, and critical thinking skills in a fun and engaging way.
Coding and Robotics: Introducing young children to basic coding concepts and robotics can spark an early interest in technology and problem-solving skills.
Research and Development

The field of ECCE is constantly evolving, and robust research and development (R&D) efforts are crucial to ensuring programs are effective, evidence-based, and meet the ever-changing needs of young children.
Brain Development Research: Research on early brain development informs curriculum design and teaching practices that best support cognitive, social, and emotional growth in young children.
Impact of Technology: We understand the appropriate use of technology in ECCE programs, maximizing its potential benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks for young learners.
Personalized Learning: Research on individual differences in learning styles and development will pave the way for personalized learning approaches that cater to each child's unique needs and strengths.
Conclusion
In conclusion, early childhood care and education (ECCE) serve as the bedrock for a child's development and future success. By fostering cognitive, social, emotional, and physical growth during the critical early years, ECCE lays the foundation for lifelong learning and well-being.
The journey towards a future-proofed ECCE system requires collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to continuous improvement. As we work together to address the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities, we pave the way for a generation of children who are not only academically prepared but also socially responsible, emotionally intelligent, and brimming with the potential to shape a brighter future for all.
The seeds sown in early childhood blossom throughout a lifetime. Let's cultivate a future where every child has the opportunity to flourish.
If you are looking for courses to start your Early Childhood Care and Education journey, you can sign up for Skilltrans courses today. We have useful courses at preferential prices.

Meet Hoang Duyen, an experienced SEO Specialist with a proven track record in driving organic growth and boosting online visibility. She has honed her skills in keyword research, on-page optimization, and technical SEO. Her expertise lies in crafting data-driven strategies that not only improve search engine rankings but also deliver tangible results for businesses.



