Business Finance: Definition, Types, Source & How to Manage
Effective financial management is the cornerstone of any successful business. Business finance is closely related to many different processes - planning, management, and control of financial resources. A company good at financial management can make wise decisions about investments, expenses, and funding.
In this article, we will explore the definition and importance of business finance, examine its different types, and discuss common sources of financing available to businesses.
Additionally, we’ll provide helpful advice to help you manage your business’s financial management, empowering you to optimize cash flow, overcome risk, and pave the way for long-term success.
What is Business Finance?

Business Finance refers to the management of money and financial resources within a business to achieve its goals, ensure efficient operations, and maximize profitability. It has many activities that work together including planning, organization, and control of financial activities (budgeting, investing, raising capital, and managing cash flow).
With the development of business, business finance always holds an important position in decision-making, resource allocation, and maintaining a company’s financial health. Based on it, businesses can fund operations, invest in future growth, and create value for stakeholders.
Sources of Business Finance

A company can raise capital from multiple sources of Business Finance to fund its operations, growth, and other financial needs. These sources are broadly categorized into internal and external financing.
Internal Sources of Finance
Internal Sources of Finance are funds that are generated within the company itself. The most common internal source is retained earnings, which are profits that the business reinvests instead of distributing as dividends to shareholders. Retained earnings are a cost-effective source since they don’t require interest payments or lead to debt obligations.
Another internal source is the sale of assets that are no longer needed by the business, providing an immediate influx of cash.
Additionally, businesses may use depreciation funds, which are amounts set aside over time to replace assets when they become obsolete or worn out.
External Sources of Finance
These are funds obtained from outside the business. They are divided into Equity Financing and Debt Financing.
Equity Financing
When businesses raise capital by selling ownership stakes in the form of shares, this money source is called Equity Financing. Companies can issue new shares to investors in exchange for funds. These exchange activities can be done through public markets for listed companies or private transactions for others.
However, selling shares dilutes ownership. Venture capital is another form of equity financing, typically used by start-ups or young companies in exchange for equity and often some level of control over business decisions.
Another option is angel investors, who are wealthy individuals providing early-stage investments. Crowdfunding has also become popular, leading to businesses raising small amounts of capital from a large pool of people through online platforms.
Debt Financing
Debt Financing occurs when a business borrows money that must be repaid over time, usually with interest. One of the most common forms of debt financing is a bank loan, where businesses borrow from a bank with agreed terms of repayment and interest.
Companies can also raise funds by issuing bonds, where investors purchase the bonds. We can understand that investors are lending money to the business in exchange for periodic interest payments and repayment of the principal amount at a future date.
Another form of debt financing is trade credit, where suppliers agree for businesses to pay for goods and services at a later date. You also should know overdrafts, which provide short-term borrowing by allowing businesses to withdraw more than what is available in their accounts, typically up to an agreed limit.
Hybrid Sources of Finance
Hybrid Sources of Finance blend elements of both debt and equity financing. For instance, convertible bonds start as debt but can be converted into equity at a later stage, providing flexibility for both the business and investors.
Besides, preferred stock offers shareholders a fixed dividend (similar to interest on debt) but typically does not come with voting rights. These hybrid options help businesses access capital while balancing the trade-offs between debt obligations and ownership dilution.
Grants and Subsidies
Grants and Subsidies are another external source of finance, particularly for businesses in specific industries or regions.
Government grants are a common form of financial assistance. The powerful benefit of this resource is that it offers businesses funds without the need for repayment. These grants have the purpose of encouraging innovation, research and development, job creation, or environmental sustainability.
While grants can be highly beneficial, they are usually tied to specific criteria and objectives. Competition for such funding can be intense.
Venture and Private Equity
Venture capital is typically sought by start-ups or businesses in their early stages. Venture capitalists provide large sums of money in exchange for equity and sometimes managerial control. This type of financing is aimed at high-growth potential businesses.
On the other hand, private equity appears to invest more in more established companies, usually with the goal of restructuring or scaling the business for profitability. Private equity investors often take a significant ownership stake and may influence the company’s strategic direction.
Choosing the Right Source of Business Finance

Choosing the right source of business finance is not an easy task. It depends on various factors, such as the business's stage of growth, the cost of capital, and the business owner's desire to retain control.
Start-ups might rely more heavily on equity financing or venture capital. Otherwise, more established companies might opt for debt financing through loans or bonds.
The choice between debt and equity also needs to consider the cost of capital - while debt requires regular interest payments, it allows the business owner to retain full ownership. Equity financing avoids debt but dilutes ownership and may give investors a say in business decisions.
Additionally, short-term finance options like trade credit or overdrafts are useful for managing immediate cash flow needs. But, long-term projects often require equity or longer-term debt options.
The Importance of Business Finance
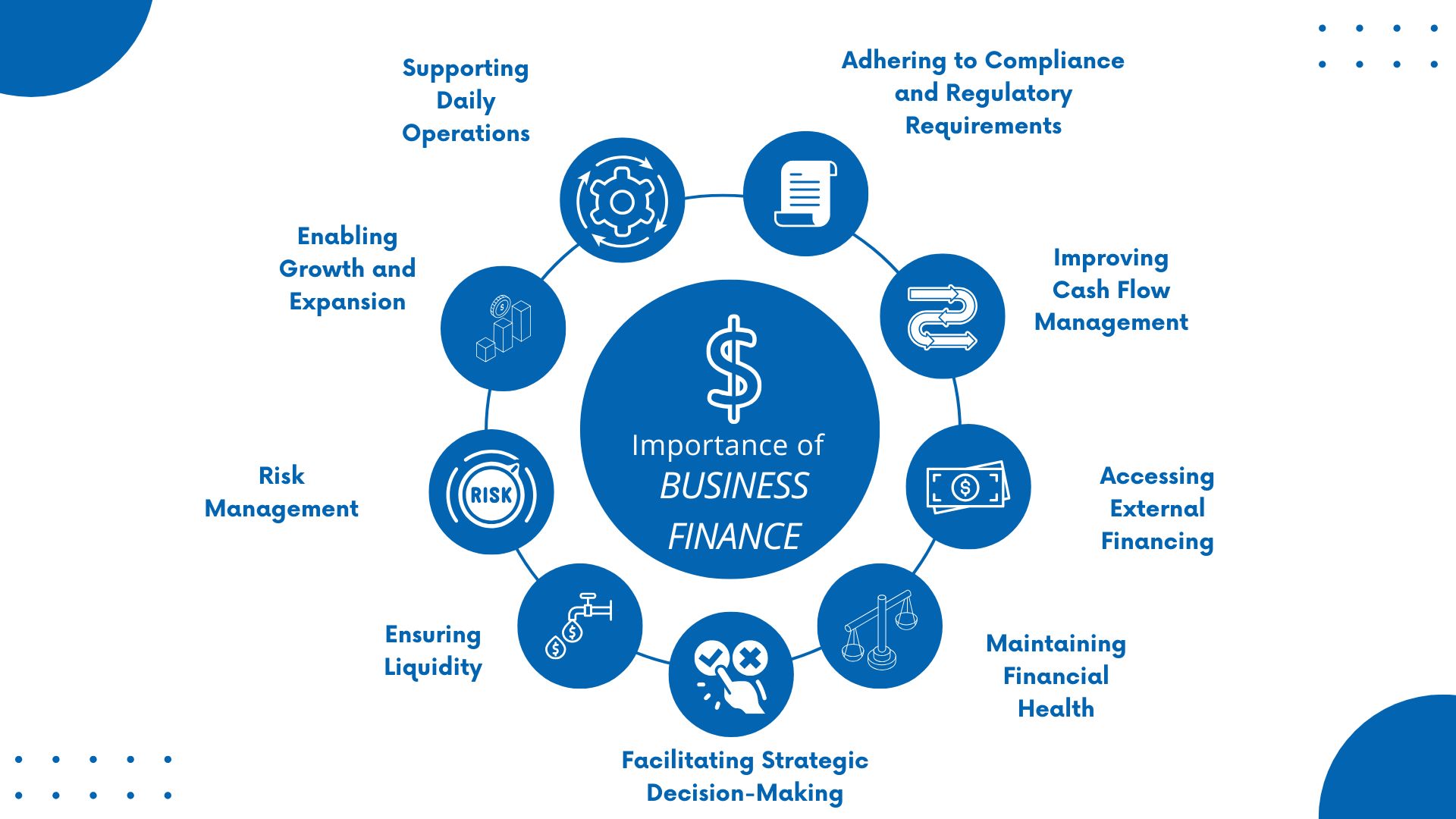
The important role of business finance cannot be denied. It sustains a company's financial health and sustainability. Effective financial management is essential for:
Supporting Daily Operations
Business finance has payment purposes the day-to-day costs of running a company. Business owners can pay salaries, purchase raw materials, and maintain inventory from business finance sources. Moreover, proper financial management makes enough working capital to meet short-term obligations and keep the business running smoothly without disruptions.
Enabling Growth and Expansion
For a business to grow, it needs funds to invest in new opportunities, whether that’s expanding into new markets, launching new products, or upgrading infrastructure and technology. Business finance provides the capital needed for these long-term investments, helping companies scale and achieve sustainable growth.
Risk Management
There are many types of risks that a business, large or small, faces. They can come from within or outside the business economic downturns, fluctuations in market demand, or unexpected expenses.
With effective financial planning, companies can set aside reserves or secure loans to handle emergencies, reducing the risk of insolvency or operational setbacks. Good financial management also supports businesses to hedge against market fluctuations and mitigate risks from factors like exchange rates or interest rates.
Ensuring Liquidity
Liquidity relates to a business's ability to convert assets into cash to meet short-term obligations. Proper business finance management sets standards that a company has enough liquidity to cover day-to-day expenses, pay suppliers, and manage any unexpected financial demands. A lack of liquidity can lead to severe operational problems or even bankruptcy, regardless of profitability on paper.
Facilitating Strategic Decision-Making
Looking at business finance, you can see the data and insights needed for informed decision-making. What you need to do is analyze financial statements, budget, and forecast future performance. Business leaders can make sound strategic decisions about resource allocation, cost management, and investment opportunities.
Maintaining Financial Health
Is the company on the right track? Are your efforts achieving the results you set out to achieve? You should monitor key financial indicators, such as profit margins, cash flow, and debt levels with the purpose of maintaining financial stability and avoiding costly mistakes. A healthy financial position also builds trust with investors, lenders, and stakeholders.
Accessing External Financing
When businesses need additional funding for growth or operations, having sound financial management and a solid track record aids in securing external financing. Lenders and investors evaluate a company’s financial health through its financial statements, credit history, and projections. Companies with strong financial management are more likely to get favorable terms on loans or attract investment.
Improving Cash Flow Management
Cash flow is the lifeblood of any business. Good financial management is a necessary condition to manage cash inflows and outflows effectively. Let's make sure that revenues are collected on time and manage expenses to avoid liquidity problems. Positive cash flow to reinvest in its business and be prepared for future challenges or opportunities.
Adhering to Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
One obligation that all businesses must complete is subject to various financial regulations and legal requirements - tax obligations, financial reporting, and accounting standards. This is also a basic way for a business to avoid penalties, audits, or legal issues. It also creates transparency and builds trust with stakeholders, including investors, employees, and customers.
In summary, business finance is the foundation for making informed decisions, managing risks, seizing opportunities, and ensuring long-term financial health. Without strong financial management, even profitable businesses can face challenges from different sides, such as cash flow shortages, operational disruptions, or failure to capitalize on growth opportunities.
Types of Business Finance

There are several types of business finance, each serving different purposes depending on the business’s needs, size, and stage of growth. These can be broadly categorized into short-term, medium-term, and long-term finance, as well as internal and external sources.
Short-Term Finance
Short-term finance is used to meet the day-to-day operational needs of a business, typically for periods of up to one year. This type of financing has the duty to maintain the business has enough liquidity to cover working capital requirements, such as inventory purchases, payment of salaries, and other operational expenses.
Trade Credit: Businesses purchase goods and services from suppliers on credit, with payment usually due in 30-90 days. You can maintain operations without immediate cash outflow.
Overdraft: Banks facilitate businesses to withdraw more money than they have in their accounts, up to an agreed limit. Businesses easily manage temporary cash shortages.
Short-Term Loans: These are loans that must be repaid within a year, typically used to cover immediate financial needs like inventory replenishment or payroll.
Factoring: Businesses sell their receivables (outstanding invoices) to a third party at a discount to get immediate cash, improving cash flow.
Medium-Term Finance
Medium-term finance is generally applied for projects or investments that will take between one to five years to yield returns. This type of finance is suitable for businesses with expansion plans, asset purchases, or working capital needs that exceed one year but are not long-term.
Term Loans: Banks or financial institutions provide loans for a specified period, usually between one and five years. They are used to finance medium-term needs such as purchasing machinery or equipment.
Leasing: Instead of purchasing assets outright, businesses can lease equipment, machinery, or vehicles. The lease payments are spread over several years, making it a flexible option for acquiring expensive assets.
Hire Purchase: Similar to leasing, hire purchase is progress paying for an asset in installments over time. Once all payments are made, ownership of the asset is transferred to the business.
Long-Term Finance
Long-term finance is used to fund major investments or projects that will take many years to complete or yield returns. This type of finance typically spans more than five years and is crucial for financing significant expansion, infrastructure, or research and development.
Equity Financing: The company raises capital by selling shares to investors. Investors gain ownership stakes in exchange for their investment, and the company does not need to repay the funds, though it shares profits with the investors.
Long-Term Loans: Banks or financial institutions provide long-term loans, usually repaid over periods of five to twenty years. The best option when using this type of finance is building facilities or acquiring other companies.
Bonds/Debentures: Companies can raise funds by issuing bonds to the public or institutions. Bonds are debt instruments where the company promises to pay interest periodically and repay the principal amount at a later date.
Venture Capital: High-growth potential businesses can attract venture capital firms that provide large sums of money in exchange for equity. This form of financing is often used by start-ups or early-stage companies.
Retained Earnings: Businesses can reinvest their profits (rather than distributing them as dividends) to finance long-term growth. Internal source of finance that avoids debt or equity dilution.
Equity Finance
Equity financing is progress in raising capital by selling ownership shares in the business. You can do this through private investors or public markets. Unlike debt, equity financing does not require repayment, but it gives investors an ownership stake in the company.
Angel Investors: Wealthy individuals provide capital to start-ups in exchange for equity. They often invest at the very early stages of the business and may also offer guidance and mentorship.
Crowdfunding: Method of raising small amounts of money from a large number of people, especially through online platforms. Crowdfunding can take the form of donations, rewards, or equity.
Private Equity: Private equity firms invest in companies in exchange for equity. Established businesses usually apply it with the goal of scaling operations or restructuring for profitability.
Initial Public Offering (IPO): When a company goes public, it sells shares to the general public for the first time through an IPO.
Debt Finance
Debt financing occurs when a business borrows money that must be repaid over time, usually with interest. Using debt financing synonyms business owner retains control of the company, though it requires regular repayments.
Bank Loans: Businesses can take out loans from banks or financial institutions. The loan amount, interest rate, and repayment terms are agreed upon in advance, and businesses are expected to make regular payments until the loan is fully repaid.
Bonds: Companies issue bonds to borrow money from investors. The company agrees to pay interest on the bonds at regular intervals and repay the principal at a specified future date.
Debentures: These are a type of long-term debt instrument that companies use to borrow money. Unlike bonds, debentures may not be backed by collateral but are based on the creditworthiness of the issuer.
Hybrid Financing
Hybrid financing instruments combine features of both equity and debt financing. These options with characteristics of flexibility for businesses in how they structure their capital.
Convertible Bonds: These are bonds that can be converted into shares of the company at a later date. They start as debt but can become equity, providing flexibility for both the issuer and the investor.
Preferred Stock: Preferred shares offer investors fixed dividends (similar to interest payments on debt) and a higher claim on assets than common shareholders, but usually without voting rights. Businesses can raise capital without giving up much control.
The type of finance a business chooses depends on various factors, including its size, stage of growth, the amount of capital needed, and the cost and terms of the financing. Short-term finance helps cover operational needs, while long-term finance is essential for strategic expansion and capital-intensive projects.
How to Manage Finance for Your Business?

Managing finance has a profound impact on the success and sustainability of a business. Good financial management helps a company maintain cash flow, fund operations, achieve growth, and respond to challenges. Here are key steps and strategies for managing business finance:
Create a Detailed Budget
A budget serves as a financial roadmap for your business. To create it, you simply plan how much money you expect to earn (revenue) and spend (expenses) over a specific period. Break down the budget into categories, such as operating costs, marketing, salaries, and utilities.
Monitor Cash Flow
Cash flow is the movement of money into and out of your business. Positive cash flow is essential for your business to meet its obligations, such as paying employees, suppliers, and debts. Implement systems to track cash flow regularly, and focus on maintaining liquidity to avoid cash shortages. You can speed up receivables (getting customers to pay faster) and delay payables (negotiating longer payment terms with suppliers) to optimize cash flow management.
Separate Personal and Business Finances
Mixing personal and business finances can lead to confusion, tax issues, and difficulty tracking business performance. Open separate business bank accounts and use dedicated credit cards for business expenses. It also ensures that personal assets are protected in case of legal or financial issues.
Track and Control Expenses
Keeping a close eye on your expenses to maintain profitability. Don't forget to review your expenses to identify areas where you can cut costs without compromising the quality of operations. For example, renegotiate contracts with suppliers, find ways to reduce utility bills, or eliminate unnecessary subscriptions and services. Implement an expense tracking system or software to make this process easier and more efficient.
Ensure Timely Invoicing and Debt Collection
Late payments from customers can negatively impact your cash flow. To avoid this, implement a clear invoicing system, resulting in clients receiving invoices promptly. Set payment terms and follow up consistently on overdue payments. You create incentives for early payments or implement penalties for late payments to improve the speed of collections.
Manage Debt Wisely
While borrowing can help a business grow, excessive debt can become a financial burden. Manage your business's debt wisely by borrowing only what you need and can comfortably repay. Always compare loan terms, such as interest rates and repayment periods, before taking on debt. If your business is struggling to meet debt obligations, consider refinancing or negotiating new terms with lenders.
Keep Accurate Financial Records
Record all transactions, including sales, expenses, and any other financial activities. Use accounting software to automate record-keeping and reduce the risk of errors. Good financial records are essential for making informed decisions, securing loans or investments, and preparing tax returns.
Invest in Your Business
Business development is a long-term process, so business reinvestment takes place regularly. You often need to purchase new equipment, expand into new markets, hire more staff, or increase marketing efforts. Investing wisely in key areas of your business can lead to future profitability and sustainability.
Review Financial Statements Regularly
Financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, provide a snapshot of your business’s financial health. Regularly reviewing these statements shows you how well your business is performing and whether you’re meeting financial goals. These documents can also help you identify trends, such as increasing expenses or declining revenues. You can address potential problems before they become major issues.
Maintain a Reserve Fund
Having a financial cushion is business support against unpredictable events such as unexpected expenses or economic downturns. Build and maintain an emergency fund that can cover several months’ worth of expenses. This reserve fund can help your business remain stable in times of uncertainty, such as a sudden drop in sales or a major equipment failure.
Explore courses from Skilltrans to gain your business finance knowledge. Please click on the course name below to learn more:
The Fundamentals Of Finance For Non-Finance Professionals
With this programme we're going to give you a simple guide to the core elements of finance that all organizations use to report and manage their results. If you ever have conversations about finance and feel even slightly out of your depth, then this introduction to the Fundamentals of Finance is for you.
Have you ever been in a position where you’re talking about your P&L, and had nagging doubts about what you were talking about? Have you ever used terms like EBIT or NPV without really understanding what they are or what they mean? Do you see mysterious financial transactions happening that affect your results, but you don’t know how (or if) you can affect them? If any of these are true, this course will remove those doubts and raise your understanding. You’ll be smarter, sound smarter, and be able to make better, faster decisions as a result.
Personal Finance For Beginners | Financial Planning 101
The Personal Finance For Beginners | Financial Planning 101 course is designed to empower individuals with the essential knowledge and skills needed to effectively manage their personal finances. In today's complex financial landscape, it is crucial to have a solid foundation in financial planning to achieve financial stability and reach long-term goals.
This course serves as an introductory guide, providing comprehensive insights into the key concepts and strategies of personal finance. Students will learn wealth building strategies, credit repair tactics, and funding secrets. Additionally, they will explore the importance of saving, investing, and managing money wisely.
Introduction to Capital Markets
Welcome to "Introduction to Capital Markets," a comprehensive journey designed to demystify the complex world of capital markets and unveil the mechanics that drive the global financial landscape. This course serves as an essential primer for aspiring financial professionals, students, and anyone with an interest in understanding how capital markets function, their role in the economy, and the key players that animate this vibrant ecosystem.
Conclusion
Sound financial management enables companies to build resilience, achieve their goals, and thrive in competitive markets. With the right approach, business finance becomes not just a tool for survival but a foundation for long-term success. To develop your business finance capabilities, don't forget an effective resource from Skilltrans courses.

Meet Hoang Duyen, an experienced SEO Specialist with a proven track record in driving organic growth and boosting online visibility. She has honed her skills in keyword research, on-page optimization, and technical SEO. Her expertise lies in crafting data-driven strategies that not only improve search engine rankings but also deliver tangible results for businesses.



